Ethics and the New Media Literacies
/All this week, the collaboration between MIT's Project nml and Harvard's Good Play Project is being spotlighted over at the MacArthur Foundation's Spotlight on Digital Media and Learning. If you don't know Spotlight, you are missing out on some of the best conversations these days about the ways that young people are learning in the context of the new participatory cultures. The two groups made a joint presentation a few weeks ago at the American Educational Researchers Association Conference in New York City.

As part of that presentation, Erin Reilly, NML's project manager, used her photoshop skills to put together this vivid representation of the collaboration we've started to build together.
The following text was written jointly by John Francis, Andrea Flores, Sam Gilbert, Lana Schwartz, and Steve Schultze
Meeting of the H's
In 2006, Henry Jenkins (Comparative Media Studies, MIT) and Howard Gardner (Harvard Graduate School of Education), both grantees of the MacArthur Digital Media and Learning initiative, met to discuss their mutual interest in ethical issues around digital media and possible opportunities for collaboration--and why not, being situated only two subway stops apart in Cambridge? More important than geography, though, were emergent complementary themes and research questions of Gardner's and Jenkins' work, which made a collaborative effort seem promising.
How has this meeting of the H's faired, and what has come out of the combined effort of Henry and Howard's teams? This week, we hope to give you an inside look at our collaboration through a series of blog posts highlighting our present accomplishments and future plans. Today, we'll start with a bit of background about our teams and the goals of our collaboration.
Two Projects, One Mission
As youth grow up in an increasingly connected environment, they are presented with a diversity of challenges. Many of these challenges arise in the context of new technologies of communication and creativity. How does digital copying relate to legacy notions of property? What do I need to know in order to collaborate with my online peers? How do I present myself online? What do I do when I encounter new communities with unfamiliar norms or ideas? In many cases, there are helpful analogies in "age old" practices. Nevertheless, the conventional wisdom of the analog world can seem like an ill fit. A more appropriate approach might frame the core skills and ethical issues within already established structures, but recognize the complications and opportunities of the contemporary media environment.
Project New Media Literacies (NML) headed by Jenkins at MIT's Comparative Media Studies program is guided by two questions:
- What do young people need to know in order to become full, active, creative, critical, and ethically responsible participants in a media-rich environment?
- What steps do we need to take to make sure that these skills are available to all?
NML uses digital media and new network technologies to help young people think about the role of media in their lives as consumers, producers, and participants
Gardner's GoodPlay Project, part of Project Zero at the Harvard Graduate School of Education, is similarly concerned with the roles that youth assume online. More specifically, the GoodPlay Project seeks to understand the ethical issues that youth face in the virtual frontier of new digital media. How models of ethics transfer from the offline to the online world--especially in the five areas of identity, privacy, authorship and ownership, credibility and participation--and how young people understand their roles and responsibilities in digital contexts are key concerns.
Together, it was decided that NML and GoodPlay would produce learning tools that help youth understand the connections between the digital media skills they learn and their roles and responsibilities as "good" cyber citizens. By integrating the GoodPlay ethical framework with the new media skill set defined by NML, the collaboration would develop activities that encourage reflection about ethical issues raised in various forms of media participation. These activities would draw on materials from the NML Exemplar Library and on data collected by the GoodPlay research team.
Let's Collaborate
In the summer of 2007, the NML and GoodPlay project teams set out to explore exactly what form our collaboration would take. We divided ourselves up into four "SuperTeams" to discuss compelling intersections between the two projects. After several weeks and many meetings, the entire group decided on a course of action for the fall: we--the "SuperQuartet" of Andrea Flores, John Francis, Steve Schultze and Lana Swartz--were challenged to generate ten high-level prototypes. After meeting with the full teams from NML-GoodPlay, we selected the best components of those prototypes for further refinement into two full learning modules. During this process, we began by considering the five core ethical issues identified in the GoodPlay white paper.
- Identity: exploring and 'playing' with different identities
- Privacy: choosing when and how to share information to whom
- Ownership/Authorship: understanding issues of control and credit for intellectual work
- Credibility: being authentic when representing one's competence and motivations
- Participation: accessing communities, understanding codes of conduct, and engaging proactively
We chose to focus on Ownership/Authorship for this first prototype development and refinement phase. This issue highlights the challenges youth face in navigating questions like "who owns the output of my work?", and "what are the appropriate means of giving credit?" Offline, these issues have a long history of legal and social norms but ethical indiscretions are commonplace. The opportunities for transgressions are compounded online by the absence of clear-cut and well-understood norms, facile technology and a multi-author model of online creation. Within this core issue of Ownership/Authorship, we integrated several skills from the New Media Literacies white paper, such as:
- Simulation: the ability to interpret and construct dynamic models of real-world processes
- Appropriation: the ability to meaningfully sample and remix media content
- Collective Intelligence: the ability to pool knowledge and compare notes with others toward a common goal
- Networking: the ability to search for, synthesize, and disseminate information
- Negotiation: the ability to travel across diverse communities, discerning and respecting multiple perspectives, and grasping and following alternative norms
In our activities, simulation helps students set up and understand real-world scenarios of ethical ownership. When facing an opportunity to sample or remix media content, students must decide what makes for acceptable and meaningful appropriation. In several instances, they must pool knowledge and compare notes with others toward a common goal. In so doing, they must exercise the ability to search for, synthesize, and disseminate information. Because ownership/authorship is a complex issue with different expectations in different situations, the activities encourage students to discern and respect multiple perspectives, and to engage alternative norms.
The combination of these issues and skills led us to four themes that we sought to address:
- Collaboration/Co-Creation/Knowledge Communities: Developing models of how to work together effectively and ethically.
- Responsibility: Highlighting the ways in which a creator has responsibilities to his/her audience, to the broader community, and to the original content and its creator (if he/she is a remixer).
- Copyright: Understanding the proper use of materials by the individual and the individual's understanding of his/her rights as a creator of content.
- "Inspired by " vs. Plagiarism: Identifying the difference between using content as a jumping off point for remixing/ creating new 'inspired by' materials vs. usurping materials as one's own creation.
We are excited with the progress that has been made, and the ways in which insights from both NML and GoodPlay informed the process. In some ways, we experienced the very concepts we were designing for, as we relied on the collective intelligence of all involved, easily negotiated differences and drew from a wide network of knowledge. It is clear that the shared authorship process can generate something greater than the sum of its parts, and that remixing and appropriation helped us iterate toward more effective activities.
But enough about us, we want to show you what we've made!
THE INSPIRED HIGHLIGHTER
When you're doing research or creating a work of art, the line between original work and copying is sometimes blurry. This activity helps "highlight" these distinctions.
In The Inspired Highlighter, students review different media samples in which one work is influenced by a former work. The two samples are presented side-by-side, and students identify the various tools that the latter author draws upon elements of the first work--characters, point-of-view, wording, theme, etc. We provide several options for teachers, such as Emma and Clueless, Gone with the Wind and Wind Done Gone, Moby Dick and a contemporary stage adaptation, Harry Potter fan fiction, and more. Students are also provided with simple summaries of concepts such as plagiarism, inspiration, copyright, public domain, and fair use. Working in groups or individually, students make comparisons across different genres, media forms, and authorial communities. This involves judging what makes for acceptable appropriation and what does not. Students identify the difference between using content as inspiration versus straightforward plagiarism.
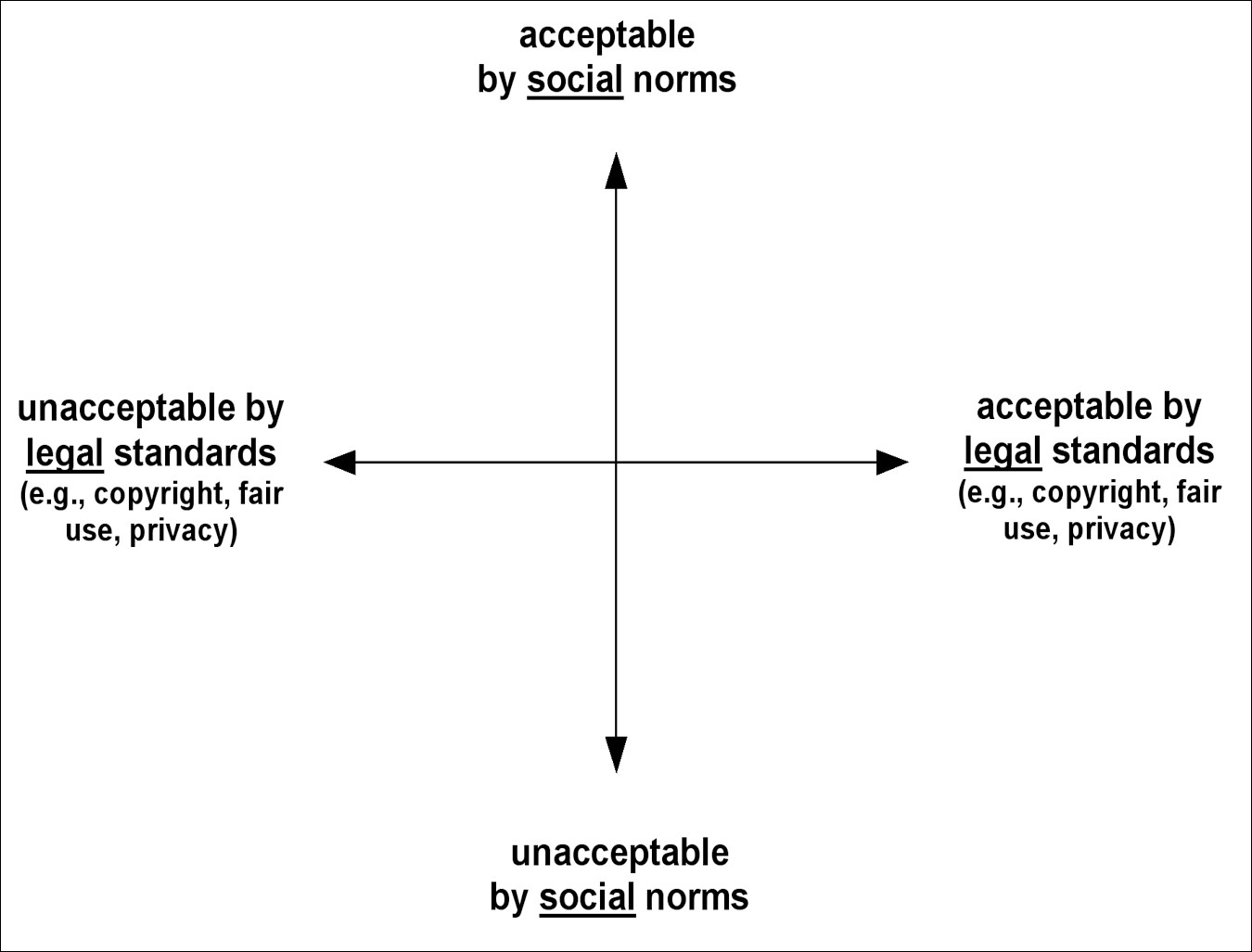
The activity uses two conceptual tools to guide students through this process. First, the students themselves place the particular instances that they discover in a simple grid that helps them the tools the author, the nature of the appropriation, and the possible motivations of the second author. The second conceptual tools is a simple graph, featuring "unacceptable copyright" on one axis and "acceptable norms" on the other. Together on the board, the class discusses where on this axis they would place the specific examples they found. Perhaps some examples are acceptable with respect to copyright law but unacceptable when it comes to authoring an original academic work. Perhaps some cases are unacceptable with a strict interpretation of copyright, but seem perfectly acceptable when considered in light of social norms.
By the end of the activity, students should be able to identify norms of ownership, tools of authorship, and instances of clear and not-so-clear plagiarism. Going forward, we hope that students will be able to highlight and consider these dilemmas not only in their school work but also in day-to-day situations.
MAD MEN
The themes of authorial responsibility and copyright are difficult concepts for many young people to grasp. In this activity, we let cows do the teaching.
In Mad Men, students role-play as advertising project managers for the 'Vegetable Growers of America' (VGA) in a campaign promoting vegetarianism. In the activity, students choose photos and music for the campaign, considering both the licensing and original intent of the musical and visual creations. For example, students have to decide whether or not using an "agency" owned photo of a cow statue at the Sri Mariamman Temple in Singapore is appropriate in this context. While the photo can be used appropriately from a copyright perspective, students must weigh the needs of the campaign, the original intent of the photo's creator, and the photo's religious context. Mad Men, then, does not simply ask students to consider copyright violations, but also encourages them to think about the potential consequences of using media for different purposes than the original artist intended.
After creating their advertising campaigns, students engage in a discussion about their decisions. In light of the music and photo choices they made for the ad campaign, they are asked to consider and articulate the likely views of different stakeholders--the VGA, the viewing public, and the original creator. Students are also prompted to consider how their concerns would change were they tasked with creating an anti-vegetarianism campaign using the same images and music. Our hopes in crafting this curriculum were twofold: 1) to expose youth to ownership norms and conventions of authorial responsibility; and 2) to scaffold youth to thoughtfully reflect on the meaning of ethical authorship and ownership decision-making in their everyday experiences.
Mad Men poses issues of responsibility and copyright in a fun and engaging role-play and a substantive experience of making distinct ethical choices. Who knew that cows could do all that?
Privacy and Publicity
Now that we've developed curricular activities that address issues of ownership and authorship, the NML-GoodPlay collaboration is focusing on to another ethical issue salient to digital youth: privacy. The Internet has changed how youth find and share information about themselves and others, challenging existing conceptions of privacy. These changes result in a lot of uncertainty about what constitute good privacy practices. Our hope is to create a curriculum that gives young people thinking tools that help them to 1) understand both the promises and the perils of disclosure online and 2) consciously adopt a set of values around what to share and what not to share online.
To start things off, the NML and GoodPlay teams recently got together for a 'group think' about privacy issues and strategies for encouraging reflection about privacy. Here are a few themes from that brainstorm that we feel will be important to address through the curriculum:
- Digital media technology has made it possible for individuals to share more about themselves to more people than ever before. It has also made it harder than ever before for individuals to control what personal information gets shared with others. Thus, while young people may have more outlets to share their thoughts, receive support and feedback, and build relationships, it's much easier for them to be taken advantage of online.
- Many young people use deception as a way of maintaining privacy. One teenager interviewed for the GoodPlay project, for example, changes the hometown listed on his facebook profile every couple of weeks so as to throw off people who might try to locate him.
- Managing privacy is rarely as simple as knowing "what to say" and "what not to say" online. It involves managing one's information across diverse communities and contexts. Often, sharing an intimate part of oneself to others online can be a positive and rewarding experience; it's when such information is copied and pasted into a new context--or shared with an unintended audience--that problems arise.
- For young people, many conflicts over privacy revolve around gossiping practices. Information is power, and young people are sometimes imprudent about sharing information so as to lift their standing in the social group.
Our heads are swimming with ideas about privacy, but we'd still love to hear some more. Do you have a great concept for an activity that capitalizes on these ideas? Any thoughts on how privacy issues manifest themselves online? Write something in the comments and continue our brainstorm!
For those of you who can't get enough of talk about new media literacies, you might want to check out this recording of a public conversation between Howard Gardner, James Paul Gee, Nichole Pinkard, Connie Yowell, and myself at AERA. Thanks to Barry Joseph and the fine folks at Global Kids for sharing this link.

